In the world of electronics, both motherboards and circuit boards play vital roles, yet they serve distinct purposes and exhibit unique characteristics. Understanding the differences between these two components is essential for engineers, designers, and consumers alike. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamental differences between motherboards and circuit boards, including their structure, functionality, and applications.
What is a Circuit Board?
A circuit board, commonly referred to as a PCB (Printed Circuit Board), is a flat, layered board used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components. It consists of conductive pathways made of copper tracks that link various components together.
Key Characteristics of Circuit Boards:
✅ Basic Structure: Typically composed of fiberglass or other insulating materials with copper layers to form conductive paths.
✅ Flexible Design: Available in different forms such as single-layer, double-layer, or multi-layer PCBs.
✅ Component Integration: Houses resistors, capacitors, transistors, and integrated circuits for specific electronic functions.
✅ Application Versatility: Used in various devices such as smartphones, industrial machines, and household appliances.
Common Types of Circuit Boards:
Rigid PCBs: Standard non-flexible boards used in most consumer electronics.
Flexible PCBs (Flex PCBs): Designed to bend and fold for applications in compact or dynamic devices.
Rigid-Flex PCBs: A hybrid design combining both rigid and flexible PCB characteristics.
What is a Motherboard?
A motherboard is a specialized type of circuit board that acts as the central hub for electronic components in a computer or other complex system. It facilitates communication between the CPU, RAM, storage devices, power supply, and expansion cards.
Key Characteristics of Motherboards:
✅ Central Control Hub: The motherboard hosts the CPU (Central Processing Unit) and manages data flow between various hardware components.
✅ Multiple Slots and Ports: Includes slots for RAM, graphics cards, storage drives, and peripherals to expand the system’s capabilities.
✅ Power Distribution: Distributes power to all key components through regulated power channels.
✅ Complex Design: Unlike standard PCBs, motherboards feature intricate layers, precise trace routing, and numerous connectors to support extensive functionality.
Common Applications of Motherboards:
Computers and Laptops: Essential for integrating hardware components.
Gaming Consoles: Handles advanced graphics and data processing.
Servers and Data Centers: Supports high-performance processing and data management.
Key Differences Between a Motherboard and a Circuit Board
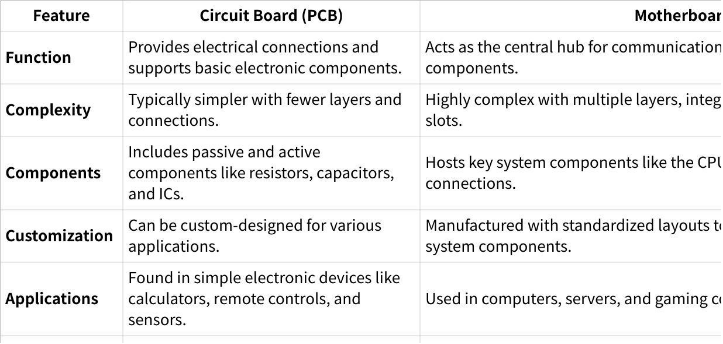
点击图片可查看完整电子表格
When to Use a Circuit Board vs. a Motherboard
Use a Circuit Board When:
You need a customized design for specific electronic functions.
The device requires minimal connectivity and component integration.
The focus is on lightweight, flexible, or low-cost design.
Use a Motherboard When:
The system requires multiple complex connections (e.g., CPU, RAM, GPU).
Advanced data communication between components is essential.
Power regulation and sophisticated heat management are crucial.
Conclusion
While all motherboards are circuit boards, not all circuit boards are motherboards. Circuit boards provide fundamental electrical pathways for simpler electronics, while motherboards are complex platforms designed to manage extensive hardware integration in sophisticated devices.
For designers and engineers, understanding the distinct roles of motherboards and circuit boards is crucial for achieving optimal performance in electronic designs. Whether you’re building a custom PCB or designing a high-performance computer, selecting the right board type will significantly impact your project’s success.